Automatic Lamination Line
Overview
This user manual provides comprehensive operational guidance for the Lamination Line. It includes detailed technical specifications, step-by-step instructions for use, and associated safety precautions to ensure efficient and safe operation.
Components and Functions
Chunker
- Function: The Chunker is designed to handle bulk dough efficiently in automated production lines. It features a hopper capacity of 50–60 kg, allowing for continuous feeding. During operation, the machine portions dough in 14 kg batches, ensuring uniformity and consistency for downstream processing. This controlled batch division enhances accuracy in portioning and maintains consistent dough structure throughout the production cycle.
- Operation: A sensor detects the dough height and activates the chunker to portion it automatically.
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure hands and clothing are kept away from the chunker zone.
- Do not override sensor functionality.
- Keep sensor surface clean and calibrated.
Extrusion Device
- Function: Pushes the dough into the feeding conveyor.
- Adjustability: Sheet thickness can be adjusted between 4 mm and 40 mm.
- Adjusting Device: Located on both ends of the extrusion machine.
- Safety Precautions:
- Stop the machine before making thickness adjustments.
- Ensure proper locking of adjusting devices before operation.
Flour Dusters
- First Duster: Applies flour to the conveyor belt to prevent dough from sticking.
- Second Duster: Applies flour to the top of the dough sheet.
- Adjustability: Both can be adjusted to user requirements.
- Safety Precautions:
- Refill dusters when the machine is stopped.
- Avoid inhaling airborne flour particles use protective masks.
Pressing Roller
- Function: Presses dough evenly to fit the multi roller.
- Safety Precautions:
- Do not attempt to clean or adjust while the roller is moving.
- Use safety guards at all times.
Multi Roller (Initial)
- Function: Reduces dough thickness from 25 mm to 8 mm.
- Features: Dual-speed control and thickness adjustment.
- Safety Precautions:
- Do not touch moving rollers.
- Use proper tools for cleaning.
Cross Roller
- Function: Expands the dough to conveyor width for even spreading.
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure dough is centered before entry.
- Use the emergency stop if alignment fails.
Marking Roller
- Function: Marks the folding position for fat insertion.
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure roller is free of debris to avoid inaccurate marking.
Folding Conveyor
- Function: Folds and seals fat into the dough.
- Adjustability: Customizable to ensure no leakage.
- Safety Precautions:
- Never manually intervene during folding.
- Confirm alignment before operation.
Fat Extruder
- Capacity: 60 kg storage; 15 kg refill cycle.
- Control: PLC and manual settings for fat-to-dough ratio.
- Safety Precautions:
- Do not exceed storage capacity.
- Use appropriate PPE when handling fats.
Laminator
- Function: Performs lamination via book or tri-fold method.
- Output: 40 mm thickness with 36 layers.
- Safety Precautions:
- Stop machine before changing lamination mode.
- Ensure proper dough consistency before lamination.
Multi Roller (Post-Lamination)
- Function: Reduces thickness to 8–10 mm (adjustable).
- Safety Precautions:
- Monitor pressure settings.
- Keep hands clear of roller entry points.
Guillotine Cutter
- Function: Cuts dough to user-defined lengths.
- Safety Precautions:
- Never place hands near the blade.
- Use emergency stop if miscut occurs.
Overlapping and Pressing Section
- Function: Aligns and presses overlapping dough joints.
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure accurate alignment before pressing.
- Use only trained personnel for this step.
Calibration Head
- Function: Calibrates dough sheet thickness precisely.
- Safety Precautions:
- Clean sensor area regularly.
- Check calibration before starting batch.
Cutting Unit
- Function: Cuts dough into desired shapes (triangle, square, round, oval).
- Safety Precautions:
- Change cutters only when power is off.
- Verify cutter sharpness and cleanliness.
Auto Panning System
- Function: Automatically pans dough pieces according to defined quantities.
- Safety Precautions:
- Ensure trays are correctly positioned.
- Do not block pan feeders.
Installation Guidelines
Proper installation is critical to ensure optimal performance, safety, and machine longevity. Follow these step-by-step instructions to install the Dough Processing and Lamination Machine.
Site Requirements
- Space: Ensure a minimum clearance of 1 meter on all sides for operation and maintenance.
- Floor: Level, non-slippery, load-bearing surface with drainage system if required.
- Ventilation: Good air circulation to maintain ambient temperature and reduce humidity.
- Lighting: Adequate lighting to inspect machine parts and monitor operations safely.
- Power Supply: Three-phase, 400V ±10%, 50/60Hz (check machine label for specific requirements).
- Water Source: If applicable, a clean water line for cleaning or steam operations.
- Compressed Air: Required if pneumatic systems are present. Pressure: 6–8 bar (check specs).
Tools and Equipment Needed
- Forklift or pallet jack for positioning the machine
- Industrial level or laser level
- Adjustable wrench set
- Screwdrivers (flathead and Phillips)
- Multimeter for electrical checks
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Unpacking and Inspection
- Unpack the machine carefully using the labeled lift points.
- Check for transit damage (dents, disconnected parts, etc.).
- Verify all components against the packing list:
- Chunker assembly
- Extruder unit
- Flour dusters
- Rollers and conveyors
- Control panel (PLC and HMI)
- Cutter and panning unit
⚠️ Important: Report any missing or damaged parts to the supplier before proceeding.
Positioning and Leveling
- Place the machine in its intended position based on the layout drawing.
- Ensure it is not placed directly under dripping water lines or HVAC units.
- Use a spirit or laser level to check that the base is even in all directions.
- Adjust leveling feet to stabilize the frame without any tilt or wobble.
Electrical Connection
- Connect to the designated power source through a circuit breaker.
- Use properly rated cables and plugs as per the machine’s manual.
- Ground the machine using the provided grounding terminal.
- Conduct an insulation and continuity check using a multimeter.
- Power on the control panel and verify basic function of PLC and HMI display.
⚠️ Only certified electricians should handle electrical installation.
Pneumatic and Fat Feeding Systems (if applicable)
- Compressed Air: Connect air hoses securely to the pneumatic control inlet.
- Fat Tank: Securely place the fat container in its holder and connect the feed pipe.
- Prime the fat pump manually before switching to auto mode.
Machine Calibration and Initial Setup
- Calibrate sensors (dough height, sheet thickness) as per HMI guide.
- Load a test recipe and run in manual mode for dry-run inspection.
- Check movement and speed of rollers, chunker, cutter, and conveyors.
- Adjust flour duster levels and verify non-sticking on belt.
Final Safety Checks
- Test all emergency stop buttons.
- Verify function of all safety interlocks and guards.
- Train at least one operator in emergency and standard startup procedure.
- Record all installation steps in the installation checklist log provided.
Detailed Step-by-Step Operation
The HMI is your primary control panel for the production line, allowing you to oversee operations, adjust settings, and diagnose basic issues.

Your HMI screen typically displays a main overview of the production line. You can move between different screens by using the arrow buttons or dedicated icons (like a house icon for the home screen) that appear on the display.
Main Production Overview Screen
This is your central hub, providing a visual representation of your production line.
- Production Line Diagram: You will see a simplified diagram of the various stages of the production process. This helps you quickly see the overall status.
- Reset Button: If the line experiences an issue or needs to be cleared, press the "Reset" button to bring the system to a safe, initial state.
- Current Product Display: The HMI will show the name of the product currently being processed or the last selected product.
Production Status Screen
This screen provides real-time information about the line's performance.
- Product Idle Time: This indicates how long the product has been in a non-moving or waiting state at a specific point on the line. It helps you identify potential bottlenecks.
- Product Speed: This shows the current operating speed of the product moving along the conveyor. You may also see indicators for the minimum and maximum allowed speeds.
- Tray Gap: This monitors the distance between trays on the conveyor. It's important for consistent product flow and helps prevent jams. You may also see indicators for optimal spacing.
Settings Screens
The settings screens allow you to fine-tune various operational parameters of the production line. Use the arrow buttons on the HMI to navigate between different pages of settings.

General Settings
- Roller On Delay: Sets the brief waiting period before the rollers begin to move after receiving a command.
- Roller Off Delay: Sets the brief period the rollers continue to operate after a stop command is issued.
- Water Spray On Delay: Controls the delay before the water spray activates.
- Water Spray Off Delay: Controls how long the water spray continues after being instructed to turn off.
- Sesame On Delay: Sets the delay before the sesame duster activates.
- Sesame Off Delay: Sets how long the sesame duster continues after being instructed to turn off.
- Tray Off Delay: Manages a delay related to how trays are released or positioned.
- Homing Offset: This is a small adjustment used to precisely set the machine's starting or "home" position.
- Product Count: Displays the number of products that have been processed on the line.
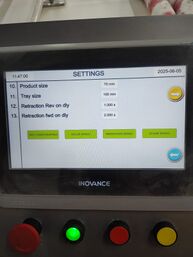
Product & Tray Settings
- Product Size: Allows you to input the dimensions for the product being manufactured, ensuring proper handling and processing.
- Tray Size: Allows you to input the dimensions of the trays used on the line, ensuring correct indexing and movement.
Bypass Controls
These controls allow you to temporarily disable specific sections or functions of the production line, which can be useful for maintenance or specific production runs.
- Tray Conveyor Bypass: Disables the tray conveyor.
- Roller Bypass: Disables the roller mechanism.
- Water Spray Bypass: Disables the water spray system.
- Sesame Bypass: Disables the sesame duster.

Recipe Selection Screen
This screen is where you choose the type of product your line will produce.
- Recipe List: A list of pre-programmed product types (e.g., "Burger," "Hot Dog") will be displayed.
- Select/Load: To choose a product, find its name in the list and press the corresponding "Load" or "Select" button. Loading a recipe will automatically configure the line's settings for that specific product, ensuring consistent quality.
I/O (Inputs/Outputs) Screens
These screens provide a diagnostic overview of the electrical signals within the machine. They are useful for troubleshooting and understanding the operational status of different components.

Inputs
Inputs are signals received by the HMI from various sensors and switches on the machine. A green indicator next to an input usually means that sensor or switch is active.
- Conveyor Servo Ready: Indicates the main conveyor motor is ready to operate.
- Retractor Servo Ready: Indicates the retraction mechanism's motor is ready.
- Dough Alignment Sensor: Detects if the dough is correctly positioned.
- Retraction Home Sensor: Indicates the retraction mechanism is in its home position.
- Retraction Stop Sensor: Detects when the retraction mechanism reaches its stopping point.
- Tray Sensor 1 & 2: Detects the presence or position of trays.
- Product Sensor: Detects the presence of a product on the line.
- Main E-Stop: Indicates if the main Emergency Stop button has been pressed.
- Main Start/Stop/Reset: Shows the status of the main control buttons.
- Pendant Stop/Start/Reset: Shows the status of control buttons on a remote pendant (if applicable).
- Roller Beam Sensor: Detects an object near the roller beam.
- Water Spray Sensor: Confirms the water spray mechanism is operating.
- Sesame Sensor: Confirms the sesame duster mechanism is operating.
Outputs

Outputs are commands sent by the HMI to activate various components and functions of the machine. A green indicator next to an output typically means that component is currently active.
- Servo Enable/Reset: Controls the main motors.
- Tower Light Indicators (Red, Yellow, Green): Controls the status lights on the machine's tower, indicating different operational states.
- Buzzer: Activates an audible alarm.
- Start Lamp: Illuminates a lamp to indicate the machine is ready to start or is running.
- Flour Duster: Activates the flour dusting mechanism.
- Water Sprayer: Activates the water spraying system.
- Fruity Duster: Activates a duster for fruit-related applications.
- Sesame Duster: Activates the sesame application mechanism.
- Retraction SLV: Controls the retraction solenoid valve.
- Tray Stopper: Controls the mechanism that stops trays.
- Tray Clamp 1 & 2: Controls the mechanisms that clamp trays.
This manual covers the essential functions of your HMI. For detailed troubleshooting or advanced operations, please refer to the complete technical documentation or contact customer support.
Step 2: Preparation and Startup
- Wear full PPE, including gloves, apron, and safety glasses.
- Power on the main PLC unit.
- Check and confirm all safety interlocks are engaged.
- Load the required recipe via the HMI interface.
- Inspect all belts, dusters, rollers, and conveyors for cleanliness and readiness.

Step 3: Dough Loading
- Load bulk dough into the chunker.
- Allow the sensor to detect the height and activate chunking.
- Monitor dough division into 14 kg portions.
Step 4: Extrusion Process
- Dough portions are pushed by the extrusion device to the feeding conveyor.
- Adjust sheet thickness (between 4–40 mm) using side knobs.
- Activate flour dusters: base duster for the conveyor, top duster for the dough.
Step 5: Pressing and First Multi Rolling
- Pressing roller evenly flattens dough.
- Multi roller reduces sheet from ~25 mm to ~8 mm.
- Adjust multi roller speed and thickness as needed.
Step 6: Cross Rolling and Marking
- Cross roller spreads dough to full conveyor width.
- Marking roller creates visible fold lines for fat insertion.
Step 7: Fat Application and Folding
- Load fat into the extruder (max 60 kg; 15 kg per cycle).
- Set fat-to-dough ratio on HMI.
- Activate fat discharge and folding conveyors to enclose fat between dough layers.
Step 8: Lamination
- Choose folding method (book or tri-fold).
- Laminate dough to form a 40 mm sheet with ~36 layers.
Step 9: Secondary Rolling and Cutting
- Post-lamination multi roller thins sheet to 8–10 mm.
- Guillotine cutter slices dough into defined lengths.
- Rest dough pieces to relax gluten.
Step 10: Overlapping and Final Rolling
- Overlap dough pieces slightly and press joints.
- Gradually reduce dough thickness using multi and cross rollers: 40 → 20 → 15 → 7 → 4 mm.
Step 11: Calibration and Shaping
- Feed 4 mm dough sheet to calibration head.
- Check for precise thickness.
- Cut into desired shapes using cutting unit (triangle, round, square, oval).
Step 12: Auto Panning
- Enable auto panning function.
- Configure tray layout and number of pieces per tray.
- Monitor panning and correct any misalignments.
Step 13: Shutdown and Cleaning
- Power off all units using main switch.
- Clean each unit thoroughly using designated tools.
- Record operation summary and report any issues.
General Safety Guidelines
- Always wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
- Ensure all emergency stop buttons are functional and accessible.
- Perform routine maintenance as per schedule.
- Keep all machine surfaces clean and free of obstructions.
- Never bypass safety interlocks or guards.
- In case of any abnormal noise or function, stop the machine immediately and inspect.
Control System
- Type: PLC-controlled.
- Interface: HMI (Human-Machine Interface) displays all parameters, sensor statuses and recipe inputs.
Safety Precautions (Before Use)
- Ensure power is properly grounded and stable.
- All safety doors and covers must be closed.
- Keep the panel area dry and clean.
- Do not bypass safety relays or modify wiring.
- In case of emergency, press the red EMERGENCY STOP immediately.
Powering Up the System
Steps:
- Turn ON the main isolator switch on the side of the PLC panel.
- The HMI screen lights up and displays the splash screen.
- Wait 10–15 seconds for system initialization.
If it doesn’t power ON:
- Check main power supply and MCB fuses inside panel.
- Ensure emergency stop is not engaged.
- Confirm that the HMI is connected to PLC (check communication cable).
- If issue persists, contact electrical support team.
Understanding the HMI Interface
Main HMI Menu will show:
- Auto Mode
- Manual Mode
- Alarm / Fault History
- Settings / Configuration
- Live Input/Output Display
Each option gives access to real-time control, monitoring, and configuration.
Running in AUTO MODE (Standard Operation)
Steps:
- Tap Auto Mode.
- Ensure all doors are closed and safety sensors show "OK".
- Tap START to begin automatic sequence.
- Machine will operate through the programmed steps:
- Conveyor runs
- Fillers operate
- Sensors trigger next step
- Monitor screen for confirmation messages like:
- “Cycle Running”
- “Completed”
If Auto Mode doesn’t start:
- Check if an error popup or alarm is displayed.
- Go to “Alarm” menu and view the exact error.
- Most common issues:
- Door not closed (safety switch open)
- Air pressure too low (check compressor)
- Previous cycle not properly reset
- After fixing, reset the alarm and try again.
Running in MANUAL MODE (Testing)
Use this mode for service, setup, or testing parts.
Steps:
- Tap Manual Mode.
- Screen displays buttons for:
- Conveyor FWD/REV
- Dosing ON/OFF
- Pusher Extend/Retract
- Motor Jog
- Tap the component you wish to test — it will operate directly.
If nothing responds in Manual Mode:
- Confirm the panel is not in E-Stop state.
- Check if air or power to actuators is available.
- Ensure PLC is not in FAULT or STOPPED state.
- Verify the I/O display shows inputs changing when you press.
Adjusting Settings (Timing, Speed, Count)
From the Settings or Configuration screen:
- Set:
- Motor delay
- Sensor delay times
- Speed levels
- Fill quantity (if available)
- Some fields require a password (ask supervisor).
If changes don’t apply:
- Press Save or Enter after each change.
- Restart the machine after changes.
- Ensure the user level is authorised for that change.
Emergency Handling
- Press the red E-STOP for immediate halt.
- All operations stop.
- To reset:
- Twist E-Stop clockwise to release.
- On HMI, tap “Clear Alarm”.
- Return to Home screen and resume normal operation.
Alarm Screen & Troubleshooting
Common faults may include:
| Alarm | Meaning | Action |
|---|---|---|
| “Sensor Not Detected” | Sensor wiring issue or blocked | Clean sensor or check wiring |
| “Door Open” | Safety limit not closed | Close door and re-check |
| “Low Air Pressure” | Air line disconnected | Connect and regulate air supply |
| “Motor Overload” | Motor jammed or over current | Switch OFF, check for mechanical jam |
🛠 Always clear the fault before restarting.
Shutting Down Safely
- Switch from Auto to Main Menu.
- Tap STOP to halt operations.
- Wait for system to cool or stop moving.
- Turn OFF the main power switch.
- Clean the panel area and close all covers.
Maintenance Guidelines
Proper and regular maintenance of the PLC panel and system ensures long-term reliability, safety, and performance.
How to Safely Clean an HMI Screen (Do's & Don'ts)
Recommended Cleaning Procedure:
- Turn OFF the machine and disconnect power before cleaning.
- Use a microfiber or lint-free soft cloth — avoid paper towels or abrasive cloths.
- Dampen the cloth slightly (do not soak).
- Gently wipe the screen in circular motions.
- Let it air dry for a few minutes before restarting the system.
Approved Solvents / Cleaners:
Use only mild and electronics-safe cleaners, such as:
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| ✅ Water-based screen cleaners | Pre-moistened screen wipes (e.g., for phones/laptops) |
| ✅ 70% Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA) | Diluted with distilled water (1:1 ratio) |
| ✅ Manufacturer-approved antistatic cleaners | E.g., Muc-Off, Screen Mom, or custom HMI-safe cleaners |
| ✅ Dry compressed air | For removing dust (no liquid contact) |
Avoid These Solvents (Can Cause Damage):
| Type | Risk |
|---|---|
| ❌ Acetone or Paint Thinner | Damages screen coating or plastic bezel |
| ❌ Benzene, Toluene, or Ammonia-based cleaners | Can cloud or crack the screen |
| ❌ Bleach or Industrial Disinfectants | Too harsh for electronics |
| ❌ Excessive Water | Can seep into the screen frame and short circuit components |
Tips:
- Never spray liquid directly on the screen — always apply to cloth first.
- Do not apply heavy pressure that may damage the touch surface.
- For tough smudges: Use 70% IPA with microfiber cloth — repeat gently.
Daily Maintenance Checklist
Perform this at the start or end of each shift:
| Task | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Check for loose wires, moisture, or abnormal lights on panel. |
| HMI Screen | Ensure touch response is smooth and screen is clean. |
| Emergency Stop Test | Press and reset to ensure system reacts instantly. |
| Air Pressure | Verify compressor and air line connections are secure. |
| Clean Surroundings | Remove dust, powder, or dough particles around panel area. |
Weekly Maintenance Tasks
Perform once a week (e.g., on Fridays or during low-load hours):
| Task | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Panel Door Seals | Wipe down with dry cloth; check for cracks or gaps. |
| Fan or Filter (if present) | Clean dust or replace air filters to avoid overheating. |
| Sensor Lens Cleaning | Gently clean proximity or photo sensors with soft tissue. |
| Button Functionality | Press all push buttons (Start, Stop, Manual) to ensure no sticking. |
| Pneumatic Check | Activate Manual Mode to confirm all cylinders operate smoothly. |
Monthly Maintenance Tasks
Perform once a month for preventive care:
| Task | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Electrical Terminal Tightening | Open panel door (with power off) and tighten all terminal screws. |
| Cable Condition | Check cables for signs of heat damage, fraying, or rodent marks. |
| PLC Status LED | Observe if PLC has any red or blinking fault indicators consult service if found. |
| HMI Firmware Backup | If applicable, export current screen settings and PLC program to USB. |
Quarterly Maintenance (Every 3 Months)
These checks help prevent long-term wear and control system failure:
| Task | Instructions |
|---|---|
| PLC Battery Check (if battery-backed) | Confirm battery voltage using diagnostic menu or multimeter. Replace if below 2.7V. |
| Grounding Inspection | Ensure all earthing wires are intact and properly connected to avoid electrical leakage. |
| Function Test in Manual Mode | Individually test all motors, cylinders, heaters, and sensors to confirm no degradation. |
| Alarm Log Review | Export and analyse any error history to detect recurring issues. |
Annual Maintenance
Call a qualified technician or your service provider for deep inspection:
| Task | Instructions |
|---|---|
| Full Panel Health Audit | Measure voltage, insulation resistance, and check for overheating marks. |
| Program Backup | Backup full PLC and HMI program to external device or cloud. |
| Software Updates | If manufacturer releases firmware updates, apply with expert help. |
| Calibration | Recalibrate dosing, filling, or cutting units to ensure precise performance. |
Things to Avoid During Maintenance
- Do not spray water or solvents directly on the panel or touchscreen.
- Do not use sharp tools near the wiring terminals.
- Do not open the panel with wet hands or while machine is running.
- Do not attempt internal PLC programming unless trained.
- Safety Precautions:
- Only trained operators should interact with the PLC/HMI.
- Regularly back up recipes and parameter settings.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Follow manufacturer’s guidelines for lubrication and part replacement.
- Use only OEM parts for replacements.
- Document all maintenance activities in a logbook.
- Contact technical support for complex troubleshooting or PLC issues.
Electrical Configuration:
Lamination line machine--12KW/3P+N/50/60 Hz/20.869A
Block line machine--10KW/3P+N/50/60 Hz/17.391A
Electric Drawings:
Block line machine
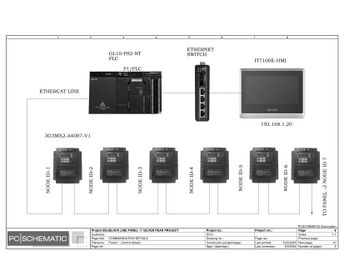
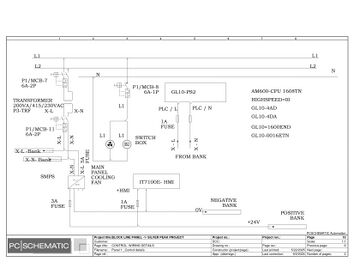
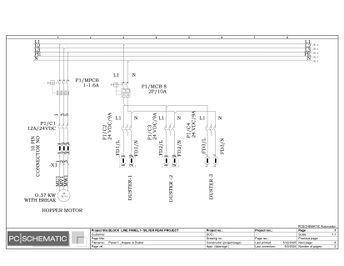



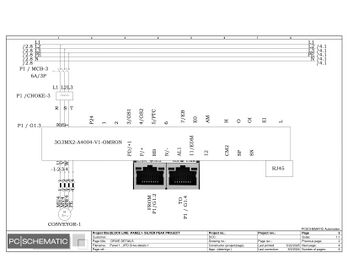


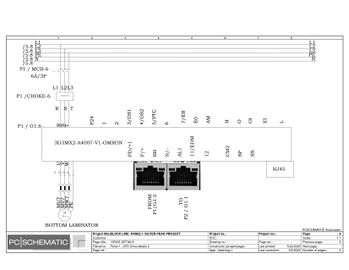


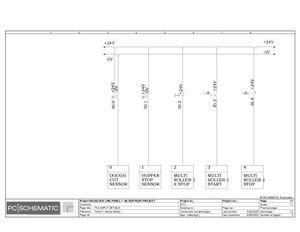
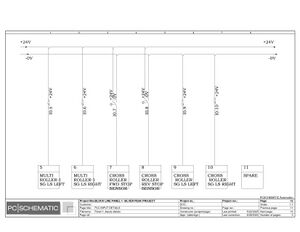
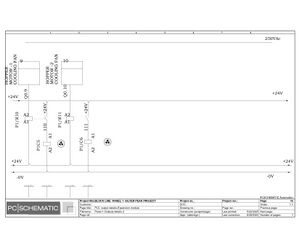
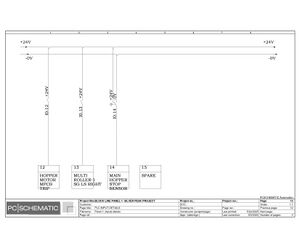
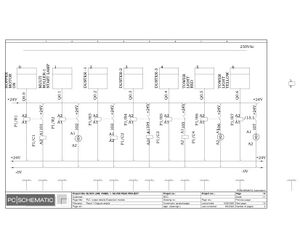
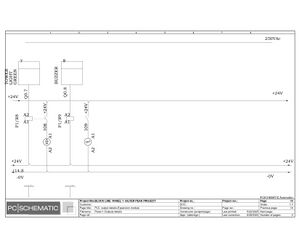









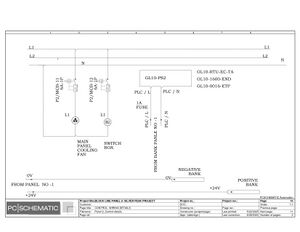
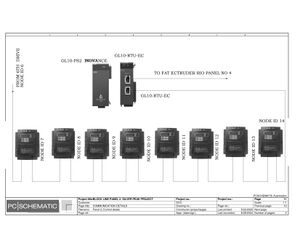
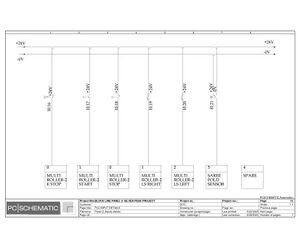
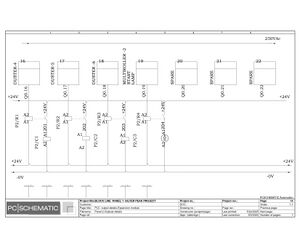
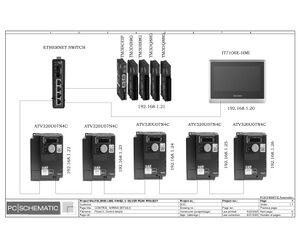
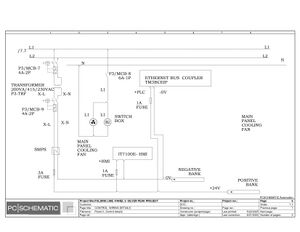


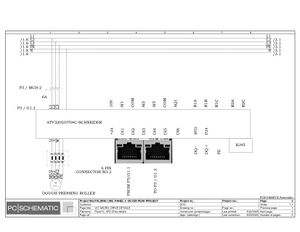



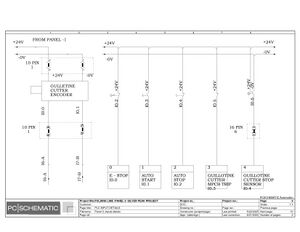
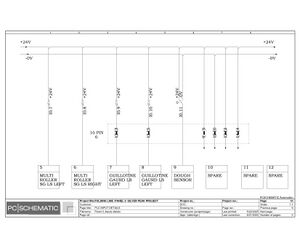
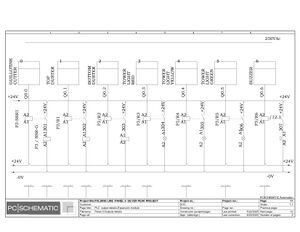
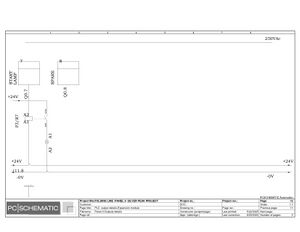
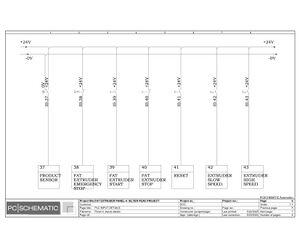
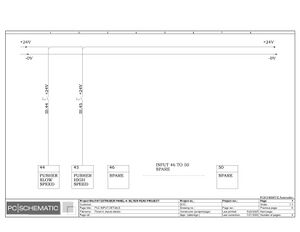






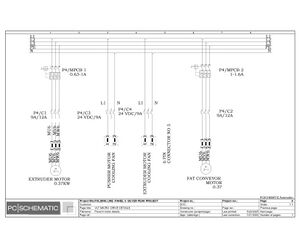
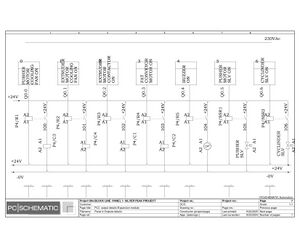
Lamination line machine:
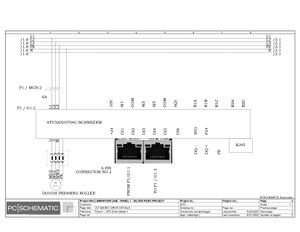
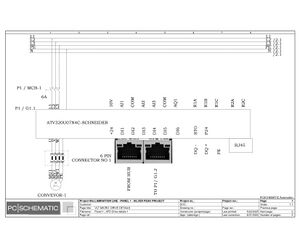
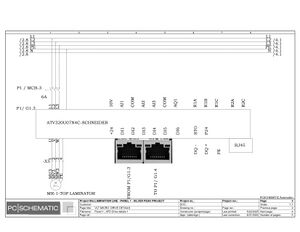
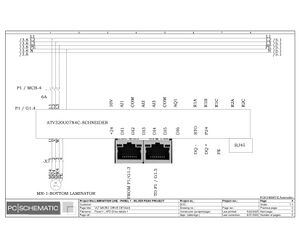
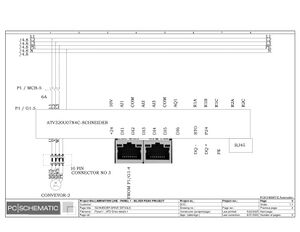
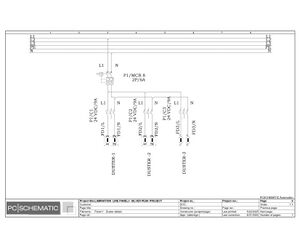
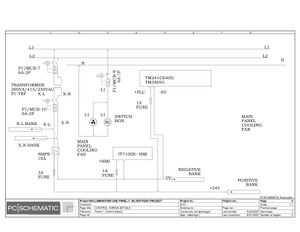
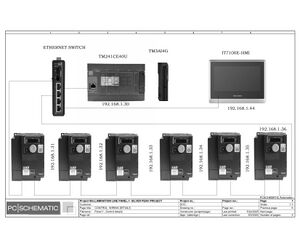

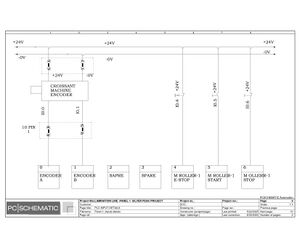
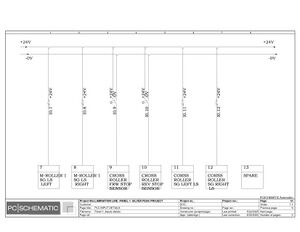
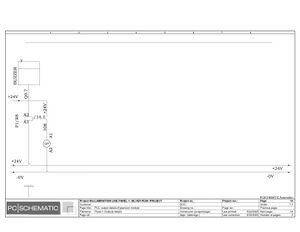
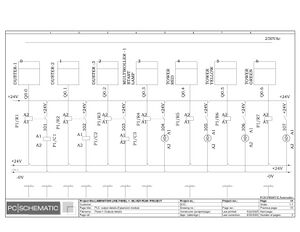
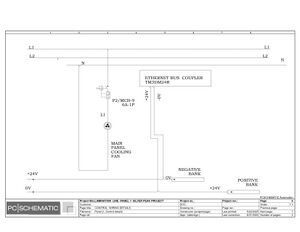
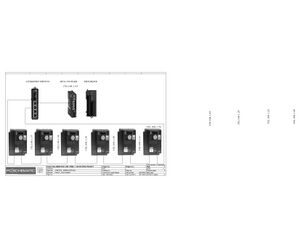
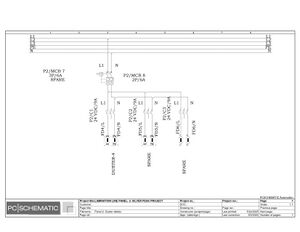
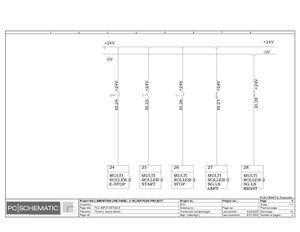
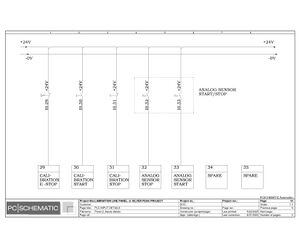





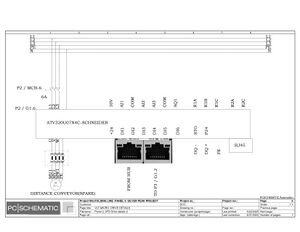
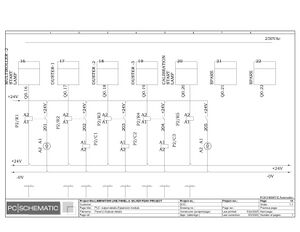
Conclusion
This machine is a sophisticated, highly adjustable system designed to produce laminated dough with precise fat incorporation and shaping. Proper understanding of each component, along with strict adherence to safety protocols, ensures optimal performance and longevity.
